Welcome To Zaara Biotech.
Zaara biotech is a Biotechnology Start-up company established
in 2016 focusing on Research in Energy and Food crisis using
Micro- Algae.
Our vision is to enhance the quality of life for the people around the globe by delivering healthy food, together with a better environment for mankind to strive for.
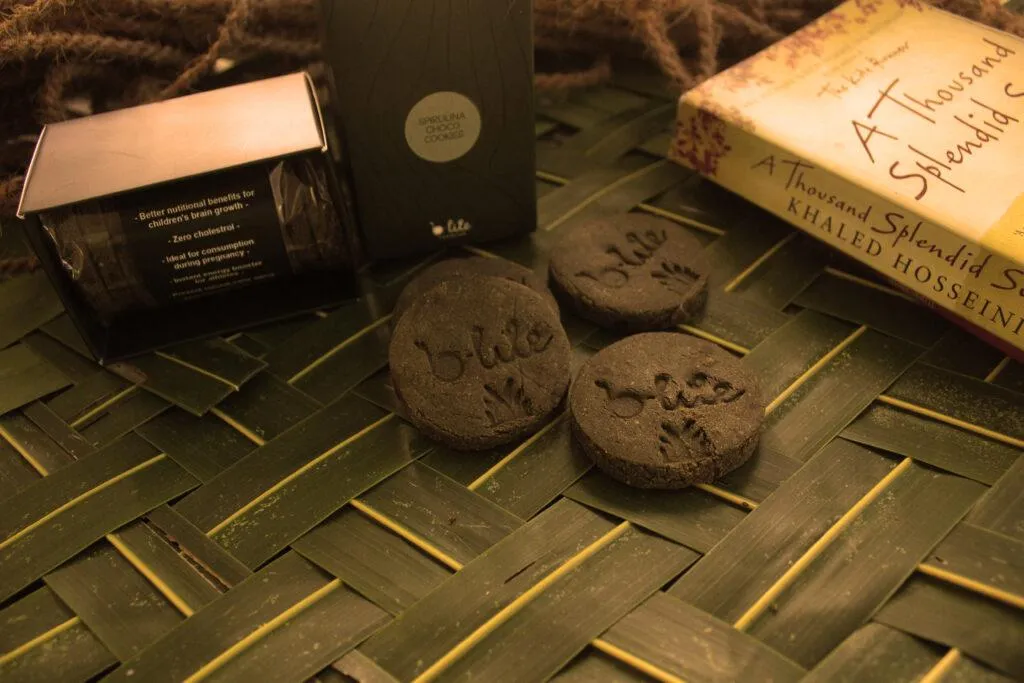
Zaara Biotech launched a number of high-nutrition products including the iconic Blite cookies.
With the collaboration from ICAR-CIFT for research and development, the company improved upon its products with algal-seaweed technology adding to its quality and taste.
With every bite of B-lite spirulina cookies, you consume digestible natural proteins, sufficient amounts of dietary fibre, calcium and iron.With its nutritional goodness, a single pack of these cookies can compensate entirely for a missed meal.

What's Hot?

From Student to Innovator: The Story Behind Aparna S. Nair's Fortified Chocolate Bar
Meet Aparna S. Nair, a biotechnology student, whose journey from an ordinary student to an extraordinary innovator is nothing short of inspiring. With guidance from Zaara Biotech Innovation Lab, she e... ...more
ZPS ,What's Hot
April 12, 2024•2 min read

Rise in temperature in Kerala and how Project Obelia could be one of the solutions!
Amidst rising temperatures and scorching heatwaves, Kerala is facing the prospect of one of its hottest summers in a decade. The combination of intense sunlight and high humidity has left residents sw... ...more
What's Hot ,Obelia
April 06, 2024•2 min read

Is Your Building Making You Sick? Recognizing and Preventing Sick Building Syndrome
Maintaining good indoor air quality: Regularly cleaning and maintaining ventilation systems, using low-VOC building materials and furnishings, and controlling indoor humidity levels. ...more
What's Hot ,Algae
March 20, 2024•3 min read

Pancreatitis Diet Guide: Optimizing Nutrition for Health & Healing
Managing pancreatitis involves a combination of medical treatment and dietary modifications. By following healthy and balanced diet rich in nutrients and antioxidants, individuals with pancreatitis ca... ...more
ZPS ,What's Hot
March 16, 2024•3 min read

Sustainability - Taste And Convenience: The New Frontier Of Food Startups
One key area of innovation is in developing plant-based snacks that not only cater to health-conscious consumers but also have a lower environmental impact. ...more
ZPS ,What's Hot
March 15, 2024•3 min read
2023: A Year of Booming Biotechnology Breakthroughs!
The recently launched R21 malaria vaccine, a promising new weapon in the fight against this deadly disease, targets multiple parasite proteins, potentially offering long-lasting protection. ...more
What's Hot
March 15, 2024•7 min read

C.E.O’s message
Zaara Biotech started out as as a college project, and despite the passage of years, we still remain steadfast in our initial motivation for its creation – the development and production of sustainable technology, emphasizing quality, efficacy, and practicality.
The FMCG sector has been the driving force behind our growth, leveraging Algal and seaweed technology. We have successfully carved our niche in the market, embodying a customer-centric approach. We go to great lengths to deliver the best nature has to offer, ensuring the highest safety and quality checks at every stage of design and production.
Our aspiration is to be a beacon of trust and sustainability, setting a standard in the biotechnology sector, with a core focus on Algal and seaweed technology.
“The unhealthy elements like cholesterol,
trans fat and white sugar are completely
absent, making b-lite cookies a great choice
for the health-conscious person”
MADE IN LOCAL
Making a great startup ecosystem in Kerala, Zaara Biotech manufactures Customized Photo bioreactors for Educational institutions and laboratories by the support of various startups across the fields of Electrical and Electronics and AI in Kerala. These sophisticated cost effective designs will flourish next generation laboratory equipment range which is made within a local ecosystem while keeping international standards.









































